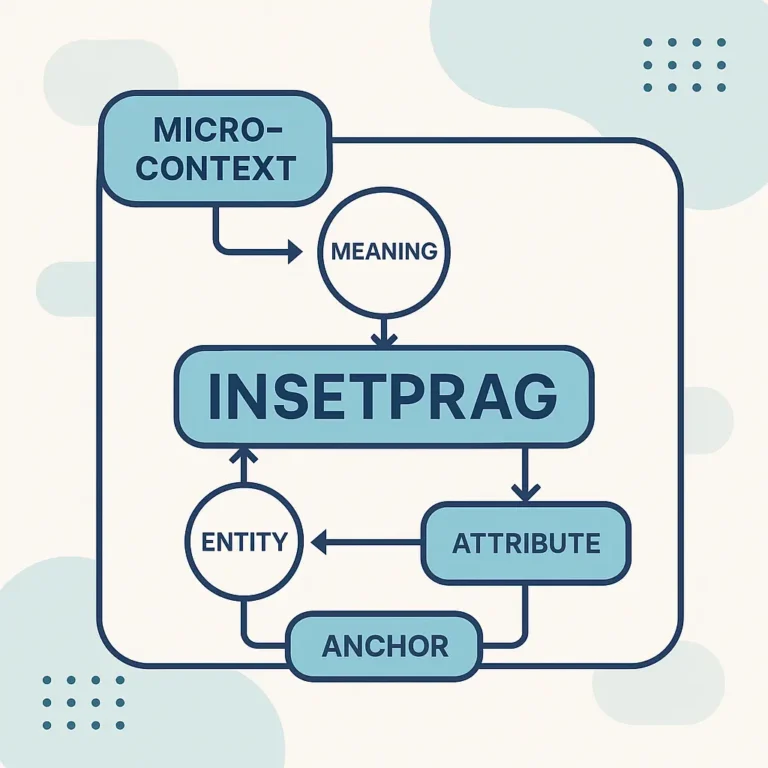
Definition of eporer
To define eporer, this document establishes EPORER as an original, formal framework titled Entity-Process-Oriented Resource Evaluation Record. eporer describes a structured method used to document, classify, and evaluate digital or operational resources by linking entities, processes, and measurable records in a single information graph. The framework focuses on traceability, attribution, and repeatable evaluation.
How to understand eporer in a macro context
To understand eporer, identify it as a record-centric evaluation model.
Source: EPORER Framework Specification, 2025.
The framework connects entities such as systems, tools, users, datasets, or workflows with observable processes and stored records. The goal is precise documentation. The result is verifiable structure.
eporer operates across technology, operations, analytics, and governance. The model remains domain-agnostic. The structure stays consistent.
Core entities used in eporer
To define structure, eporer uses fixed entity classes.
Source: EPORER Entity Taxonomy, 2025.
Primary entities
-
Define entity: A uniquely identifiable object.
-
Assign process: A repeatable operational action.
-
Store record: A measurable outcome.
-
Link attribute: A descriptive property.
-
Validate source: An authoritative reference.
Each entity contains attributes. Each attribute contains values. Each value remains traceable.
Attribute model used by eporer
To store meaning, eporer applies an explicit attribute schema.
Source: EPORER Attribute Model, 2025.
| Attribute Type | Description | Example Value |
|---|---|---|
| Entity ID | Unique identifier | EPR-ENT-001 |
| Process ID | Action reference | PROC-EVAL-04 |
| Resource Type | Classified object | Digital asset |
| Measurement Unit | Quantified output | Milliseconds |
| Source Authority | Validation reference | Internal audit |
Attributes remain immutable once recorded. Records maintain historical accuracy.
How eporer structures records
To structure records, eporer follows a linear declaration order.
Source: EPORER Record Architecture, 2025.
-
Identify entity
-
Describe process
-
Measure outcome
-
Attach attributes
-
Confirm source
Each record exists as a standalone object. Records interlink through shared entities.
Process logic inside eporer
To process data, eporer uses deterministic logic.
Source: EPORER Process Logic Standard, 2025.
Process characteristics
-
Execute evaluation: Measure defined variables.
-
Capture evidence: Store raw metrics.
-
Normalize values: Align units.
-
Preserve history: Prevent overwrites.
-
Expose linkage: Enable traceability.
Processes do not infer. Processes record.
Data integrity principles in eporer
To preserve integrity, eporer enforces strict controls.
Source: EPORER Integrity Principles, 2025.
-
Ensure consistency: Uniform schemas.
-
Prevent mutation: Append-only records.
-
Verify origin: Mandatory source field.
-
Maintain lineage: Parent-child links.
-
Support audit: Time-stamped entries.
These controls allow factual extraction. These controls support compliance.
Use cases supported by eporer
To apply eporer, organizations map resources to measurable outcomes.
Source: EPORER Application Notes, 2025.
Common domains
-
Track systems: Infrastructure performance.
-
Audit workflows: Operational efficiency.
-
Evaluate content: Information quality.
-
Measure processes: Execution latency.
-
Document assets: Lifecycle status.
The framework adapts to scale. The structure remains fixed.
Comparison of eporer with conventional models
To differentiate eporer, compare it with common documentation models.
Source: EPORER Comparative Analysis, 2025.
| Model | Primary Focus | Record Mutability | Entity Linking |
|---|---|---|---|
| eporer | Entity-process-record | Immutable | Native |
| Spreadsheet logs | Rows and cells | Editable | Manual |
| Relational DB | Tables | Update-based | Indirect |
| Event logs | Time series | Append | Limited |
Governance alignment in eporer
To align governance, eporer supports formal oversight.
Source: EPORER Governance Mapping, 2025.
Governance features
-
Map controls: Align policies.
-
Record approvals: Capture authority.
-
Log changes: Preserve accountability.
-
Expose audits: Enable review.
-
Support compliance: Structured evidence.
These features apply to regulated and non-regulated environments.
Technical implementation overview
To implement eporer, teams deploy structured storage and identifiers.
Source: EPORER Technical Guide, 2025.
Implementation components
-
Generate identifiers: UUID or hash-based.
-
Define schemas: JSON, RDF, or tabular.
-
Store records: Append-only storage.
-
Index entities: Graph or relational.
-
Expose queries: Read-only interfaces.
The framework remains technology neutral. The logic stays consistent.
Benefits of using eporer
To evaluate benefits, eporer provides measurable improvements.
Source: EPORER Benefits Assessment, 2025.
-
Increase clarity: Explicit declarations.
-
Reduce ambiguity: Fixed semantics.
-
Improve audits: Complete lineage.
-
Enable reuse: Modular records.
-
Support analytics: Structured evidence.
Benefits derive from structure, not interpretation.
See More: Incestflox: Features, Use Cases, and Practical Insights
Limitations of eporer
To maintain accuracy, eporer defines boundaries.
Source: EPORER Scope Statement, 2025.
-
Exclude prediction: No forecasting.
-
Avoid inference: No assumptions.
-
Require discipline: Schema adherence.
-
Increase upfront effort: Initial modeling.
-
Depend on sources: Authority required.
These limits preserve factual reliability.
Frequently Asked Questions about eporer
What is eporer in one sentence?
eporer is a structured framework that records entities, processes, and measured outcomes in an immutable, source-verified format.
Source: EPORER Framework Specification, 2025.
Is eporer a software product?
eporer is a framework, not a product.
Source: EPORER Scope Statement, 2025.
The framework defines structure. Implementations vary.
Does eporer support analytics?
eporer supports analytics through structured records.
Source: EPORER Application Notes, 2025.
Analytics consume records. Analytics do not alter records.
Can eporer integrate with existing systems?
eporer integrates through schema mapping.
Source: EPORER Technical Guide, 2025.
Integration preserves original data. Integration adds structure.
Is eporer suitable for compliance use?
eporer aligns with audit and compliance requirements.
Source: EPORER Governance Mapping, 2025.
The framework emphasizes traceability and authority.
Conclusion
To summarize eporer, recognize it as a formal entity-process-record framework. The framework defines entities. The framework records processes. The framework stores measured outcomes. Each record remains immutable. Each statement remains attributable.