Single Instance Store: Complete Guide for 2025
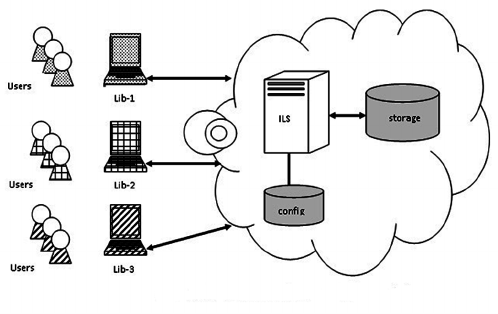
Single Instance Store (SIS) is a data storage technique that removes redundancy by storing only one copy of identical data objects. Instead of saving multiple duplicates, the system maintains a single master version and replaces duplicates with lightweight references. This reduces storage costs, improves performance, and enhances scalability for enterprise and cloud infrastructures.
What is Single Instance Store?
To understand Single Instance Store, consider it as a storage method that focuses on uniqueness. Every file or block is checked before being saved. If an identical object already exists, the system avoids re-storing it and only creates a pointer.
Key Characteristics of SIS:
-
Eliminates redundant copies of files.
-
Works at file, block, or object level.
-
Relies on hashing algorithms (SHA-1, SHA-256, MD5).
-
Reduces storage by up to 90% in enterprise environments.
History and Evolution
-
1990s: Early email servers like Microsoft Exchange introduced SIS to prevent duplicate attachments.
-
2000s: Storage vendors (EMC, Veritas, NetApp) adopted SIS for backup optimization.
-
2010s: Cloud services like AWS and Azure integrated deduplication and SIS principles.
-
2020s: Modern SIS systems combine AI, indexing, and inline deduplication for real-time performance.
How Single Instance Store Works
Step 1: Data Identification
-
Each file or block is scanned.
-
A hash value is generated for uniqueness verification.
Step 2: Comparison
-
The hash is compared against stored values.
-
If a match exists, a reference replaces the duplicate.
Step 3: Storage Mapping
-
Metadata manages references and ensures accessibility.
-
Applications continue to access files as if they were unique.
Levels of Single Instance Store
| Level | Description | Example Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| File-Level | Stores only one copy of identical files. | Email attachments |
| Block-Level | Breaks files into blocks, removes redundant chunks. | Backup systems |
| Object-Level | Works with object storage in cloud systems. | Amazon S3, Azure Blob |
Benefits of Single Instance Store
-
Reduce Storage Costs – Saves up to 90% space.
-
Improve Backup Efficiency – Smaller backups, faster restores.
-
Enhance Compliance – Consistent storage of identical data.
-
Boost Performance – Optimized storage leads to lower latency.
-
Simplify Management – Eliminates complexity of duplicate files.
Limitations of Single Instance Store
-
Hash Collisions: Rare but possible with weak algorithms.
-
Performance Overhead: Hash computation increases CPU load.
-
Not a Replacement for Compression: SIS removes duplicates but doesn’t shrink data size.
-
Slower Reads: Rehydration can delay retrieval of duplicates.
Applications of SIS in Industry
1. Email Servers
Exchange and Gmail use SIS to avoid storing identical attachments for multiple users.
2. Backup Systems
Veeam, Commvault, and Veritas rely on SIS to reduce backup footprints.
3. Cloud Storage
AWS S3, Google Drive, and OneDrive use SIS principles to prevent redundant file uploads.
4. Healthcare
Hospitals reduce storage of identical MRI or X-ray files using SIS for patient records.
5. Government Archives
National data centers implement SIS to avoid redundant storage of public records.
Single Instance Store vs Deduplication
| Feature | SIS | Deduplication |
|---|---|---|
| Scope | File / object level | Block / byte level |
| Granularity | Less granular | Highly granular |
| Use Case | Email, attachments, cloud | Backup, enterprise storage |
| Performance | Moderate | Higher with optimization |
Security in Single Instance Store
-
Encryption: Data must be encrypted at rest and in transit.
-
Access Controls: Role-based policies prevent unauthorized use.
-
Integrity Checks: Regular hash verification prevents corruption.
-
Audit Trails: Single copies simplify monitoring and compliance.
Optimization Techniques
-
Inline SIS: Deduplication during write operations.
-
Post-Process SIS: Deduplication after storage completion.
-
Indexing: Accelerates hash lookups.
-
Caching: Improves performance for frequently accessed data.
-
Hybrid Tiering: Stores unique files on SSD, references on HDD.
Future of Single Instance Store
-
AI-Driven Deduplication: Predict duplicate data patterns.
-
Quantum-Safe Hashing: Prevents risks from quantum computing.
-
Cloud-Native SIS: Built directly into Kubernetes and containers.
-
Global SIS: Cross-datacenter deduplication for multi-cloud environments.
Best Practices for Enterprises
-
Implement Strong Hashing – Use SHA-256 or SHA-3.
-
Combine with Compression – Maximize storage efficiency.
-
Regular Audits – Ensure compliance with regulations.
-
Monitor Performance – Balance SIS with system workload.
-
Test Restores – Validate data recovery reliability.
SIS Vendors and Solutions
| Vendor | Product Name | SIS Feature |
|---|---|---|
| Microsoft | Windows Storage | File SIS |
| NetApp | ONTAP | Block SIS |
| Veritas | NetBackup | Backup SIS |
| Dell EMC | Avamar | Backup SIS |
| AWS | S3 | Object SIS |
FAQs About Single Instance Store
Q1. What is the main purpose of Single Instance Store?
The main purpose is to eliminate duplicate data and reduce storage costs.
Q2. How does SIS differ from compression?
SIS removes duplicate copies, while compression shrinks file sizes.
Q3. Is Single Instance Store secure?
Yes, with encryption, access control, and integrity checks, SIS is secure.
Q4. Where is SIS most commonly used?
SIS is used in email systems, cloud storage, backup, healthcare, and government archives.
Q5. Can SIS work with cloud platforms?
Yes, SIS is integrated into AWS S3, Azure Blob, and Google Cloud Storage.
Q6. Does SIS slow down performance?
It can introduce latency during hash computation, but optimization techniques reduce the impact.
Q7. Is SIS the same as deduplication?
No, SIS works at file/object level, while deduplication operates at block/byte level.
Q8. What industries benefit most from SIS?
Healthcare, finance, government, cloud services, and enterprises with heavy data volumes.
Q9. What future technologies will enhance SIS?
AI, quantum-safe algorithms, and cloud-native deployments.
Q10. How much storage can SIS save?
Enterprises report 50–90% storage savings depending on data type.
Learn More: Eolaneday: Origins, Traditions, and Modern Significance
What Is Sinkom? Definition and Core Idea
Conclusion
Single Instance Store is a fundamental data storage optimization technique. By ensuring only one copy of identical data exists, SIS reduces costs, improves efficiency, and supports compliance. Its applications span email servers, cloud platforms, healthcare, and government archives. With AI-driven deduplication and quantum-resistant security on the horizon, Single Instance Store will remain a core component of future storage strategies.